Biomaterials
Advanced materials for healthcare
Biomaterials are natural, biological or synthetic materials that are designed and manufactured to be fully compatible with biological tissues in the human body and with defined functions for the benefit of patients. They provide options for better regeneration of burnt skin or broken bones, in-situ drug delivery, continuous and real-time detection of abnormal molecules in the blood for early diagnosis of diseases, better implants improving the recovery after trauma or surgical tumor removal.
Biomaterials are advanced materials that have been engineered to be compatible with biological tissues and organs (for example, muscle, bone, pancreas or hearth). They can be either synthetic or biological – their main characteristics being their biocompatibility in a defined application. The area of biomaterials science and technology has been growing for the last 50 years. It encompasses biology, chemistry, medicine, tissue engineering and indeed material sciences.
Contrary to biological materials which are exclusively produced by biological systems (for example, muscle or bone), biomaterials can be either synthetic or biological.
What do advanced materials bring to healthcare?
Biomaterials offer a huge range of new possibilities to repair the human body, prevent pathologies and monitor the healing process or chronic health conditions of patients:
- Coatings and surface treatments on conventional alloys can inhibit implant rejection or corrosion, confer anti-bacterial properties to a material, promote integration in targeted tissues.
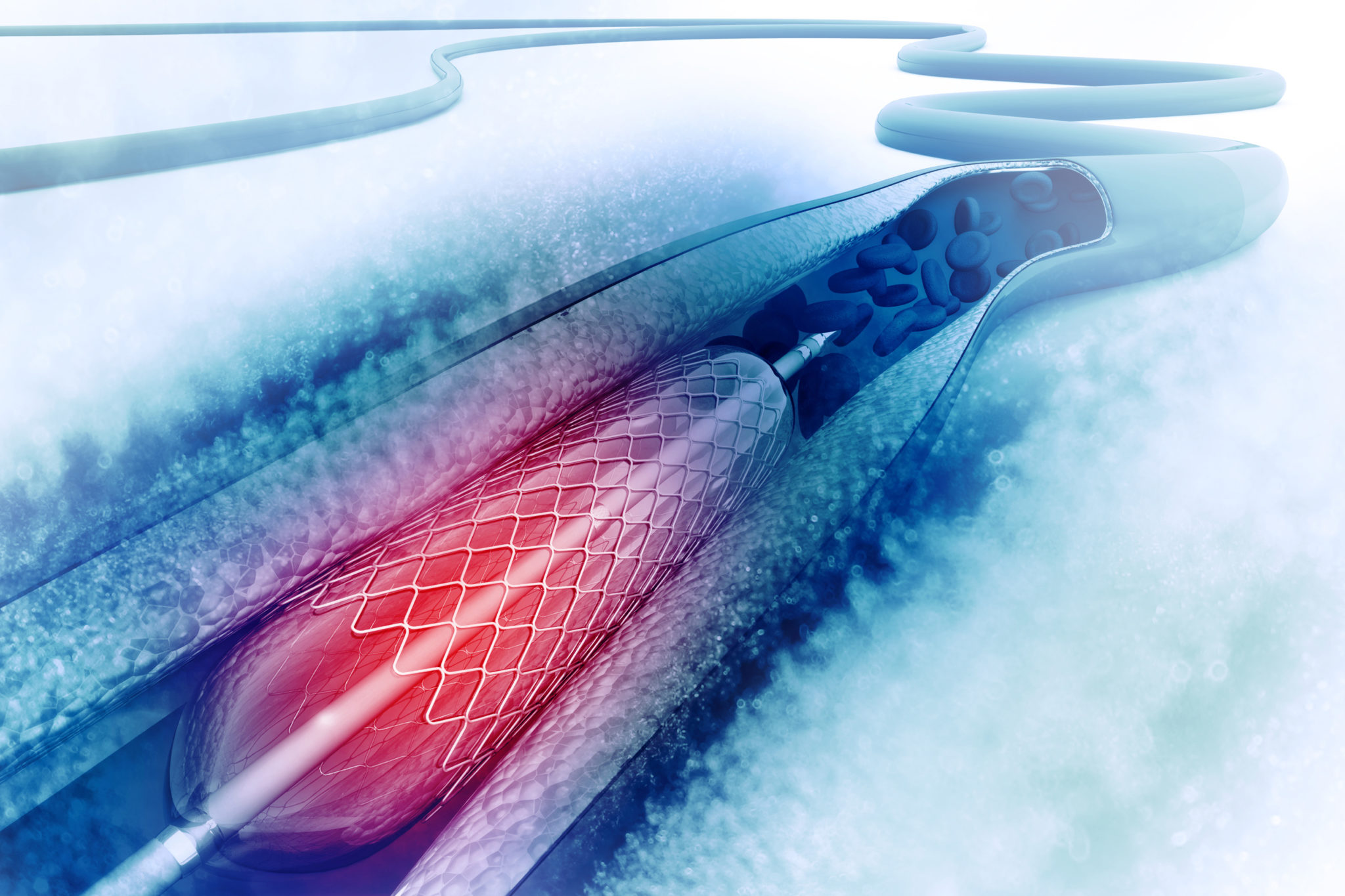
- Multifunctional implants, such as stents, joint implants and contact lenses can help the repair of tissues, deliver drugs to a specific target and serve as prosthesis at the same time.
- 3D printing allows an optimised design of prosthesis.
- Functionally Graded Materials (FGM), characterised by a variation of properties when dimensions vary, mimic natural bones and teeth, allowing implants or scaffolds to replace or repair those.
- Biodegradable ceramics, metals, composites and polymeric biomaterials are naturally eliminated by the body after they have fulfilled their mission.
- Devices coupled with stimuli response activation improve diagnosis, therapy and support research against pathologies through real time monitoring of physiopathology.
- Nano-enabled biomaterials: see fact sheet on Nanomedicine
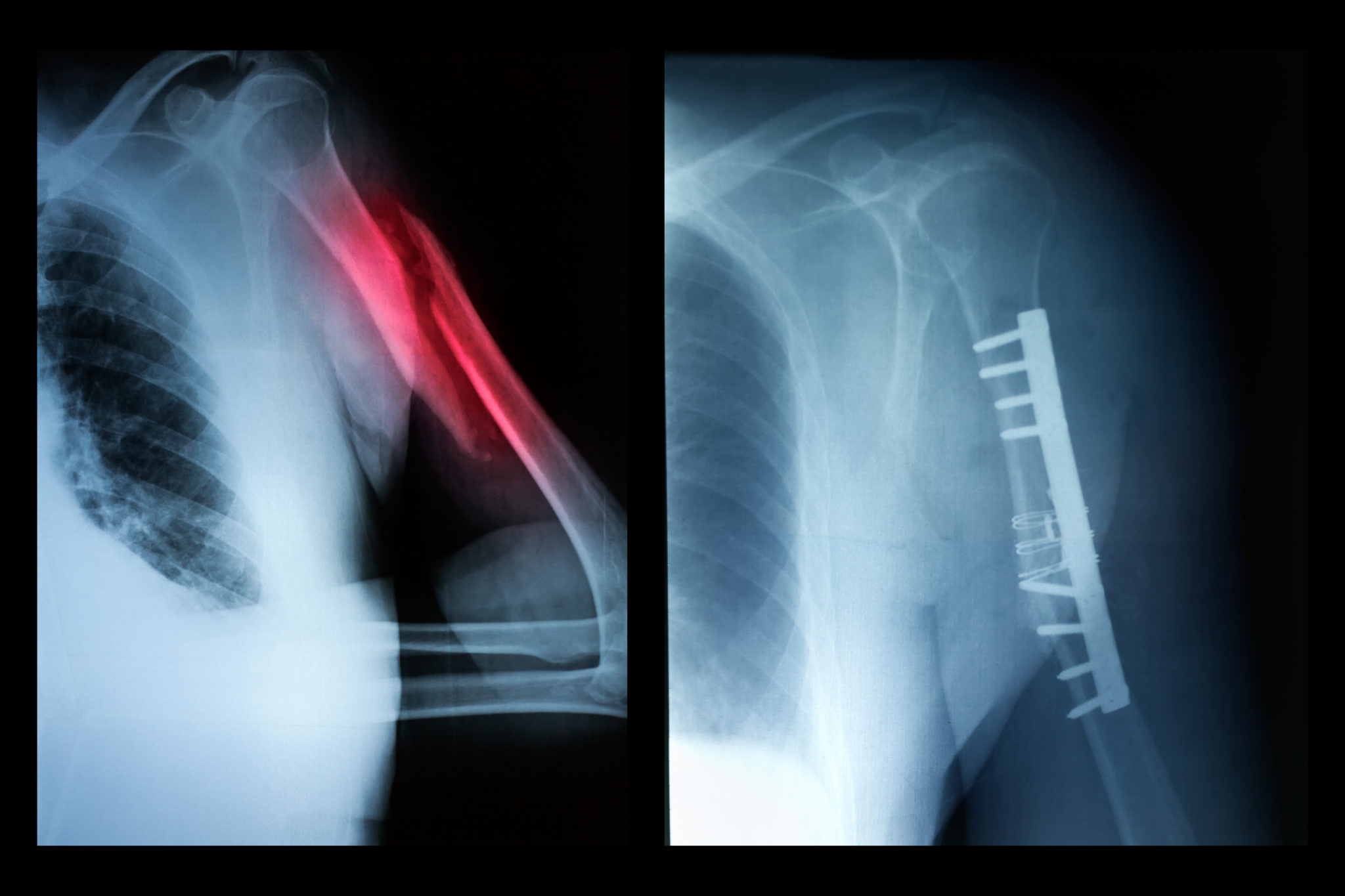
Easier and more efficient implant and prosthesis integration and biocompatibility
Continuous prevention, better diagnosis and improved treatment thanks to multifunctional implants
Boosted R&D in healthcare thanks to the real-time identification of biomarkers
Smart drug delivery
More reliable implants through reduction of material defects
Biomaterials applications
The global nanomedicine market
2016
US$70
billion
%
Annual growth rate
2020
US$149
billion
How will NOBEL support the biomaterials community?
The European project NOBEL is a Coordination and Support Action (CSA) under Horizon 2020 aiming to help the convergence of advanced materials with other key enabling technologies with applications in healthcare: nanomedicine, photonics, robotics and digital health.
European Technology Platforms (ETPs) represent each individual technological community at the European level and help bridging those communities with the European Commission. Six ETPs that have applications in healthcare are associated to NOBEL: ETP-Nanomedicine, Photonics21, EU-Robotics, EU-MAT, the European Society of Biomaterials and the ETP for Smart Systems Integration (EPoSS). The NOBEL Project provides them with a meeting space and dissemination by organising annual meetings of their representatives and sharing information from each of them to the HealthTech community.
The NOBEL Project provides the ecosystem with strategic documents on the future of HealthTech in Europe by combining the inputs of all its Associated Partners in a single vision: the Continuum of Care, a vision for the future of healthcare in Europe.
All terms are defined in the Glossary.
The list of technologies/products/companies described in these fact sheets is not exhaustive and does not intend to promote any particular actor of the HealthTech community nor to advertise particular product/company.