What are Health Technologies?
We all benefit from Health technologies (HealthTech) almost daily. They refer to any technology, device or digital solution designed to improve the health of patients. HealthTech applications can be found in very common medical devices like glasses or condoms, as well as in high-tech instruments like pacemakers, neuro-stimulators and MRI systems. HealthTech already allow to diagnose and treat millions of patients worldwide, every year, for virtually all diseases. A new medical revolution is ongoing, triggered by HealthTech. Smart medical devices start to integrate nanomaterials, biomaterials, robotic parts, high-tech microscopes and artificial intelligence. Today, researchers, entrepreneurs and clinicians work together to create the healthcare of the future: organ-on-chip can model the disease of each individual patient, an robotic exoskeleton piloted by the patient’s brain signal can make paralysed people walk again.
HealthTech refer to any technology, device or digital solution designed to improve the health of patients.
HealthTech development leads to:
- Medical devices, i.e. products intended to perform a therapeutic or diagnostic action on human beings by physical means.
- In vitro diagnostic systems, non-invasive assays analysing biomarkers of pathologies in biological samples
- Digital health solutions.
Health technologies bring major benefits:
Continuous prevention of diseases
Earlier, faster and more accurate diagnosis
More efficient and safer therapies
Long-term and/or real-time monitoring of patient after treatment
R&D in healthcare
Smart hospital management
There are more than 500.000 medical devices currently used in healthcare worldwide. HealthTech is therefore already helping to diagnose, treat and monitor patients, fighting against virtually every disease or pathologic disorder.
HealthTech can be found in very familiar products such as glasses, syringes or latex gloves, as well as high-tech devices, like for instance full body 3D scanners or neurostimulators. Here are some examples of the diversity of medical devices:

Glasses
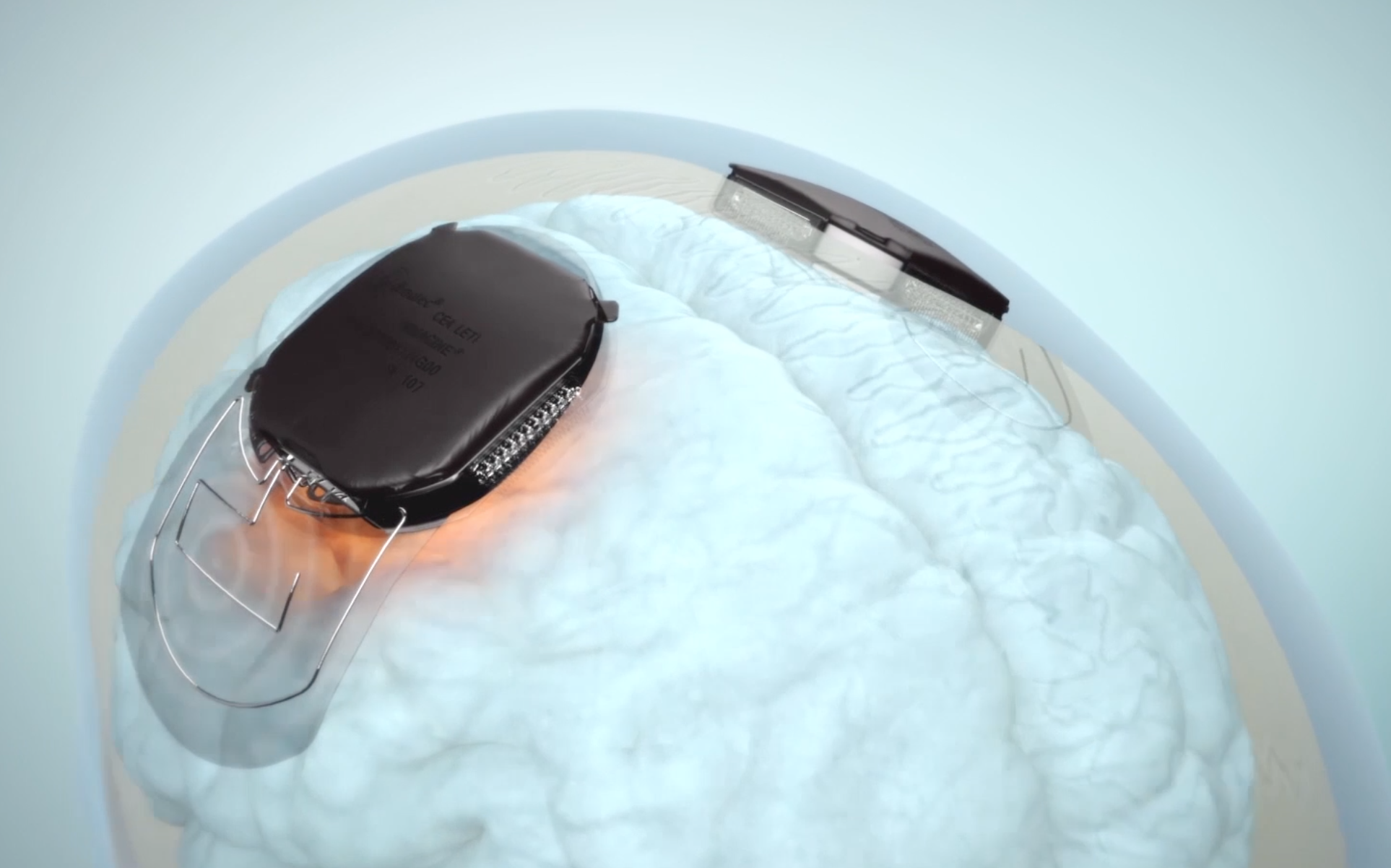
Pacemaker
Magnetic Resonance Imaging

Automated in vitro diagnosis systems
Nanocarriers for smart drug delivery
Multi-disciplinary HealthTech approaches trigger a medical revolution
All emerging technologies shown below have applications in healthcare. NOBEL acts to boost the convergence in Europe of these individual technologies into smart medical devices: new devices that will revolutionise medicine by providing more personalised, less invasive, safer and much more efficient approaches for patients.
A medical revolution is ongoing thanks to Health Technologies, as illustrated on the scheme below. A wide set of medical breakthroughs is coming, from hardware to software.
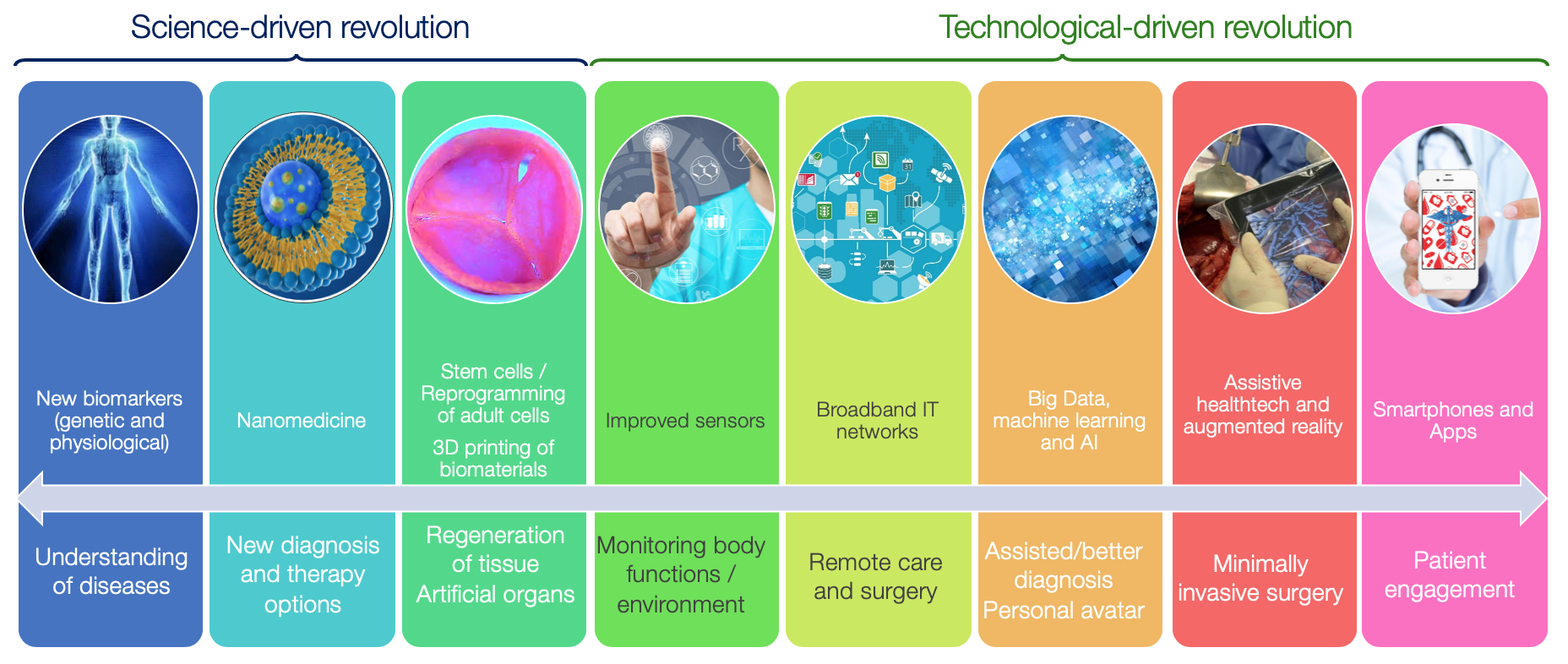
Convergence of health technologies opens new horizons
All terms are defined in the Glossary.
The list of technologies/products/companies described in these fact sheets is not exhaustive and does not intend to promote any particular actor of the HealthTech community nor to advertise particular product/company.